

Caution: This page is about SHA256 instructions of Intel SHA Extensions. They do not work on processors that do not support this feature.
As for SHA256, FIPS 180-4 issued by the government agency of the United States, is the original specification.
The following is the algorithm to calculate the hash value from the pre-processed 64-BYTE (16-DWORD) message blocks, defined in page 22 and 23 of FIPS 180-4.


SHA256MSG1 and SHA256MSG2 instructions help the calculation of A above.
SHA256RNDS2 instrucion helps the processing of B above.
The expression of A is the calculation of DWORD values to be appended to the pre-processed 16-DWORD message block, to generate the 64-DWORD W array.
To calculate the SHA hash on x86/x64, the byte order within each DWORD has to be swapped, because SHA calculations are based on big-endian. SHA256 instructions do not do the swapping automatically.
The expression of A specifies to add W[t-16], W[t-15], W[t-7] and W[t-2] and set the sum to W[t]. Before the addition, W[t-15] and W[t-2] have to be converted by the sigma functions defined in FIPS 180-4.
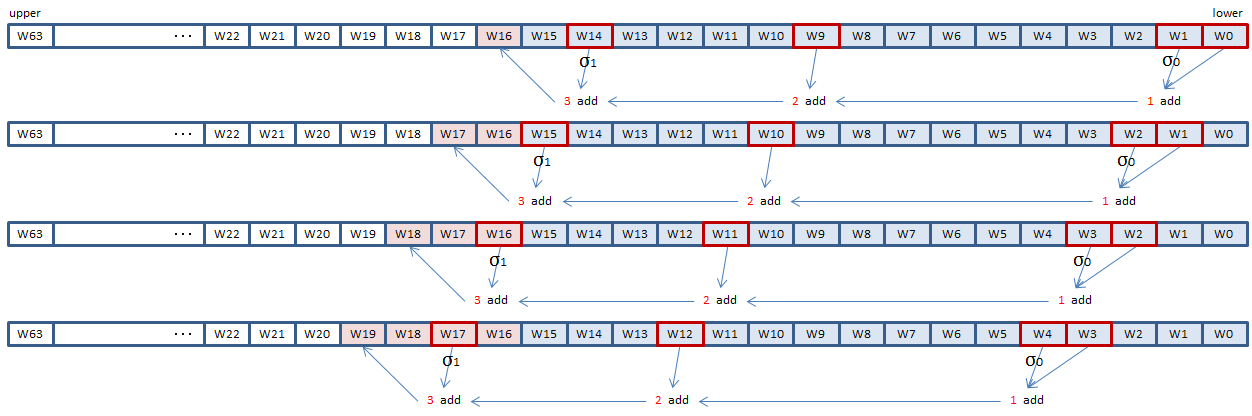
SHA256 instructions make it possible to do this, four elements at a time.
SHA256MSG1 instruction does the sigma conversion and addition of 1 in the illustration above.
SHA256MSG2 instruction does the sigma conversion and addition of 3.
Ordinary SIMD PADDD instruction can do the addition of 2.
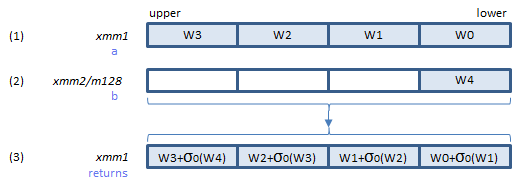
Does the sigma and addtion of 1 and returns the result in (3).
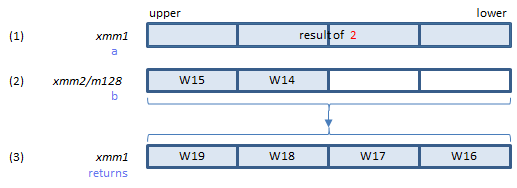
Does the sigma and addition of 3, and returns the result in (3).
Inputs: (1) = result of 2. (2) = the elements of the W array.
B loops through all 64 elements of the W array to update eight state variables a, b, c, d, e, f, g and h.
Executing SHA256RNDS2 instruction once, 2 rounds of the loop are processed.
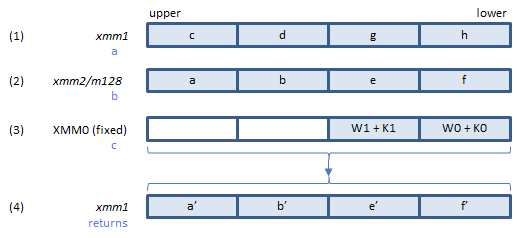
Does 2 rounds of B loop to calculate updated state variables.
Inputs: (1) = the state variables c, d, g, h. (2) = the state variables a, b, e, f. (3) = elements of the W array + elements of the K array.
Output: (4) = the state variables a', b', e', f' updated after 2 rounds of the loop.
The K array is a 64-DWORD constant array defined in page 11 of FIPS 180-4. Each element of the K array is to be added to the corresponding element of the W array to make the input data (3).
The updated state variables c', d', g', h' are not returned by this instruction, because they are equal to the input data (2) (the state variables a, b, e, f before the 2 rounds).
#pragma once
#include <intrin.h>
class SHA256H
{
protected:
// Message block
static const size_t MBYTES = 64;
unsigned char msgbuf[MBYTES];
size_t msgbuf_count; // length (in byte) of the data currently in the message block
unsigned __int64 total_count; // total length (in byte) of the message
// Intermediate hash
__m128i h0145; // h0:h1:h4:h5
__m128i h2367; // h2:h3:h6:h7
public:
SHA256H() { Initialize(); }
~SHA256H() {}
void Update(const void* buf, size_t length);
void Final(void* digest);
protected:
void Initialize();
void ProcessMsgBlock(const unsigned char* msg);
};
#include <memory.h> #include "SHA256H.h" // K Array (see FIPS 180-4 4.2.2) static const union { unsigned __int32 dw[64]; __m128i x[16]; } K = { 0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5, 0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174, 0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da, 0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967, 0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85, 0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070, 0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3, 0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2, }; // Initial hash value (see FIPS 180-4 5.3.3) #define H0 0x6a09e667 #define H1 0xbb67ae85 #define H2 0x3c6ef372 #define H3 0xa54ff53a #define H4 0x510e527f #define H5 0x9b05688c #define H6 0x1f83d9ab #define H7 0x5be0cd19 void SHA256H::Initialize() { h0145 = _mm_set_epi32(H0, H1, H4, H5); h2367 = _mm_set_epi32(H2, H3, H6, H7); msgbuf_count = 0; total_count = 0; } void SHA256H::Update(const void* buf, size_t length) { const unsigned char* p = (const unsigned char*)buf; total_count += length; // If any bytes are left in the message buffer, // fullfill the block first if (msgbuf_count) { size_t c = MBYTES - msgbuf_count; if (length < c) { memcpy(msgbuf + msgbuf_count, p, length); msgbuf_count += length; return; } else { memcpy(msgbuf + msgbuf_count, p, c); p += c; length -= c; ProcessMsgBlock(msgbuf); msgbuf_count = 0; } } // When we reach here, we have no data left in the message buffer while (length >= MBYTES) { // No need to copy into the internal message block ProcessMsgBlock(p); p += MBYTES; length -= MBYTES; } // Leave the remaining bytes in the message buffer if (length) { memcpy(msgbuf, p, length); msgbuf_count = length; } } void SHA256H::Final(void* digest) { // Add the terminating bit msgbuf[msgbuf_count++] = 0x80; // Need to set total length in the last 8-byte of the block. // If there is no room for the length, process this block first if (msgbuf_count + 8 > MBYTES) { // Fill zeros and process memset(msgbuf + msgbuf_count, 0, MBYTES - msgbuf_count); ProcessMsgBlock(msgbuf); msgbuf_count = 0; } // Fill zeros before the last 8-byte of the block memset(msgbuf + msgbuf_count, 0, MBYTES - 8 - msgbuf_count); // Set the length of the message in big-endian __m128i tmp = _mm_loadl_epi64((__m128i*)&total_count); tmp = _mm_slli_epi64(tmp, 3); // convert # of bytes to # of bits const __m128i total_count_byteswapindex = _mm_set_epi8(-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7); tmp = _mm_shuffle_epi8(tmp, total_count_byteswapindex); // convert to big endian _mm_storel_epi64((__m128i*)(msgbuf + MBYTES - 8), tmp); // Process the last block ProcessMsgBlock(msgbuf); // Get the resulting hash value. // h0:h1:h4:h5 // h2:h3:h6:h7 // | // V // h0:h1:h2:h3 // h4:h5:h6:h7 __m128i h0123 = _mm_unpackhi_epi64(h2367, h0145); __m128i h4567 = _mm_unpacklo_epi64(h2367, h0145); // Swap the byte order const __m128i byteswapindex = _mm_set_epi8(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15); h0123 = _mm_shuffle_epi8(h0123, byteswapindex); h4567 = _mm_shuffle_epi8(h4567, byteswapindex); __m128i* digestX = (__m128i*)digest; _mm_storeu_si128(digestX, h0123); _mm_storeu_si128(digestX + 1, h4567); } void SHA256H::ProcessMsgBlock(const unsigned char* msg) { // Cyclic W array // We keep the W array content cyclically in 4 variables // Initially: // cw0 = w3 : w2 : w1 : w0 // cw1 = w7 : w6 : w5 : w4 // cw2 = w11 : w10 : w9 : w8 // cw3 = w15 : w14 : w13 : w12 const __m128i byteswapindex = _mm_set_epi8(12, 13, 14, 15, 8, 9, 10, 11, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 3); const __m128i* msgx = (const __m128i*)msg; __m128i cw0 = _mm_shuffle_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128(msgx), byteswapindex); __m128i cw1 = _mm_shuffle_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128(msgx + 1), byteswapindex); __m128i cw2 = _mm_shuffle_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128(msgx + 2), byteswapindex); __m128i cw3 = _mm_shuffle_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128(msgx + 3), byteswapindex); // Advance W array cycle // Inputs: // CW0 = w[t-13] : w[t-14] : w[t-15] : w[t-16] // CW1 = w[t-9] : w[t-10] : w[t-11] : w[t-12] // CW2 = w[t-5] : w[t-6] : w[t-7] : w[t-8] // CW3 = w[t-1] : w[t-2] : w[t-3] : w[t-4] // Outputs: // CW1 = w[t-9] : w[t-10] : w[t-11] : w[t-12] // CW2 = w[t-5] : w[t-6] : w[t-7] : w[t-8] // CW3 = w[t-1] : w[t-2] : w[t-3] : w[t-4] // CW0 = w[t+3] : w[t+2] : w[t+1] : w[t] #define CYCLE_W(CW0, CW1, CW2, CW3) \ CW0 = _mm_sha256msg1_epu32(CW0, CW1); \ CW0 = _mm_add_epi32(CW0, _mm_alignr_epi8(CW3, CW2, 4)); /* add w[t-4]:w[t-5]:w[t-6]:w[t-7]*/\ CW0 = _mm_sha256msg2_epu32(CW0, CW3); __m128i state1 = h0145; // a:b:e:f __m128i state2 = h2367; // c:d:g:h __m128i tmp; /* w0 - w3 */ #define SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cwN, n) \ tmp = _mm_add_epi32(cwN, K.x[n]); /* w3+K3 : w2+K2 : w1+K1 : w0+K0 */ \ state2 = _mm_sha256rnds2_epu32(state2, state1, tmp);/* state2 = a':b':e':f' / state1 = c':d':g':h' */ \ tmp = _mm_unpackhi_epi64(tmp, tmp); /* - : - : w3+K3 : w2+K2 */ \ state1 = _mm_sha256rnds2_epu32(state1, state2, tmp);/* state1 = a':b':e':f' / state2 = c':d':g':h' */ /* w0 - w3 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw0, 0); /* w4 - w7 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw1, 1); /* w8 - w11 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw2, 2); /* w12 - w15 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw3, 3); /* w16 - w19 */ CYCLE_W(cw0, cw1, cw2, cw3); /* cw0 = w19 : w18 : w17 : w16 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw0, 4); /* w20 - w23 */ CYCLE_W(cw1, cw2, cw3, cw0); /* cw1 = w23 : w22 : w21 : w20 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw1, 5); /* w24 - w27 */ CYCLE_W(cw2, cw3, cw0, cw1); /* cw2 = w27 : w26 : w25 : w24 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw2, 6); /* w28 - w31 */ CYCLE_W(cw3, cw0, cw1, cw2); /* cw3 = w31 : w30 : w29 : w28 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw3, 7); /* w32 - w35 */ CYCLE_W(cw0, cw1, cw2, cw3); /* cw0 = w35 : w34 : w33 : w32 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw0, 8); /* w36 - w39 */ CYCLE_W(cw1, cw2, cw3, cw0); /* cw1 = w39 : w38 : w37 : w36 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw1, 9); /* w40 - w43 */ CYCLE_W(cw2, cw3, cw0, cw1); /* cw2 = w43 : w42 : w41 : w40 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw2, 10); /* w44 - w47 */ CYCLE_W(cw3, cw0, cw1, cw2); /* cw3 = w47 : w46 : w45 : w44 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw3, 11); /* w48 - w51 */ CYCLE_W(cw0, cw1, cw2, cw3); /* cw0 = w51 : w50 : w49 : w48 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw0, 12); /* w52 - w55 */ CYCLE_W(cw1, cw2, cw3, cw0); /* cw1 = w55 : w54 : w53 : w52 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw1, 13); /* w56 - w59 */ CYCLE_W(cw2, cw3, cw0, cw1); /* cw2 = w59 : w58 : w57 : w56 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw2, 14); /* w60 - w63 */ CYCLE_W(cw3, cw0, cw1, cw2); /* cw3 = w63 : w62 : w61 : w60 */ SHA256_ROUNDS_4(cw3, 15); // Add to the intermediate hash h0145 = _mm_add_epi32(state1, h0145); h2367 = _mm_add_epi32(state2, h2367); }